How Thermocouples Work – basic working principle + RTD
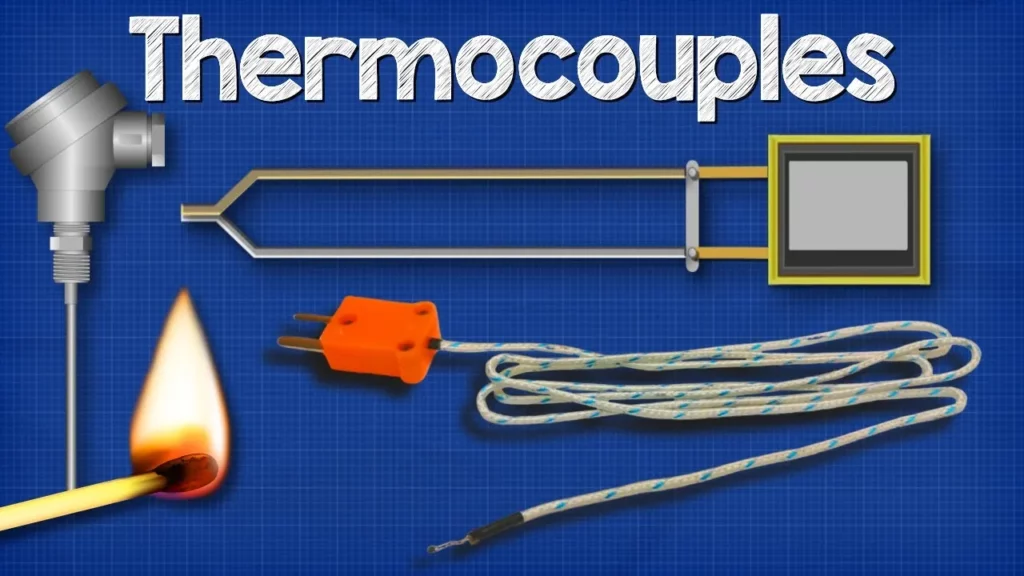
This lesson provides an overview of thermocouples and Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), two essential devices for temperature measurement. Thermocouples operate on the Seebeck effect, generating a voltage from the junction of two different metals exposed to heat, while RTDs measure temperature by detecting changes in the resistance of materials, typically platinum. Both devices are crucial in various applications due to their accuracy, reliability, and ability to function in diverse environments.
How A Car Battery Works – basic working principle
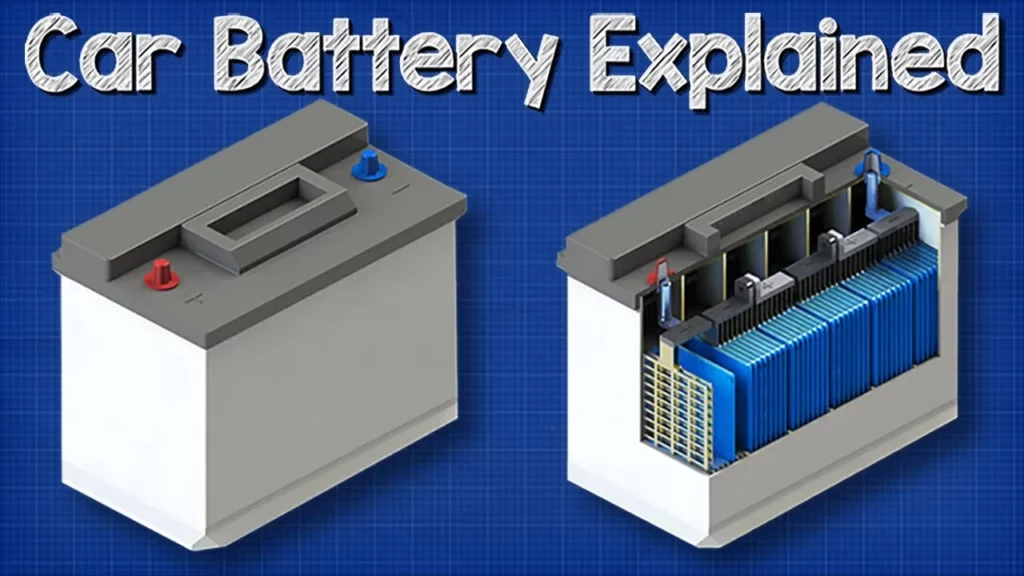
The lesson explains the basic working principle of a 12-volt lead-acid car battery, highlighting its role in starting and powering a vehicle. It details the battery’s structure, the chemical reactions that occur within it, and how it stores and converts energy. Additionally, the lesson covers the recharging process facilitated by the alternator and provides insights on checking battery health.
Variable Air Volume – VAV system HVAC
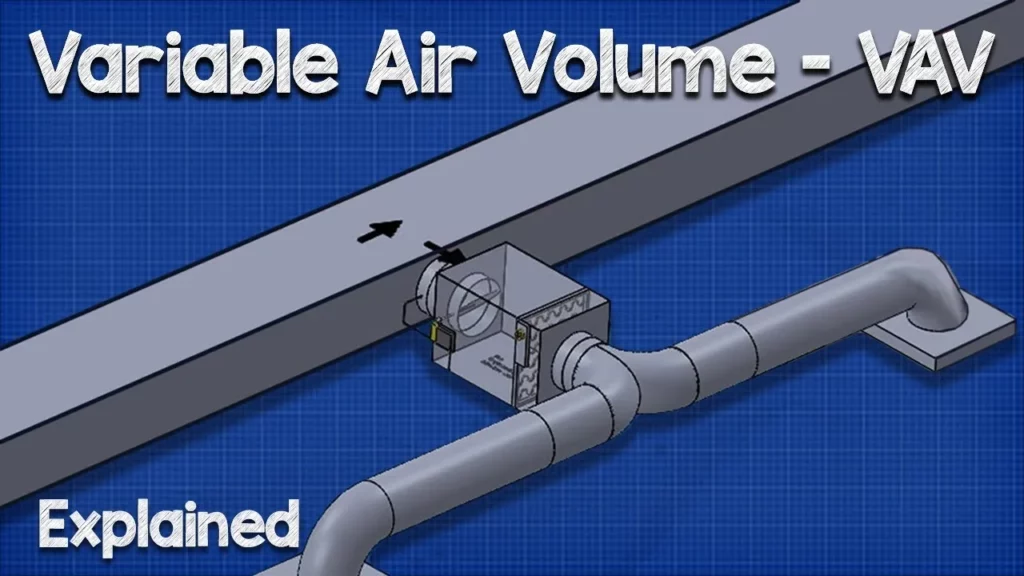
This lesson provides an overview of Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems, which are essential for efficient climate control in modern HVAC applications, particularly in office buildings. VAV systems allow for individual temperature regulation in different rooms through the use of VAV boxes connected to a central air handling unit, optimizing energy use by adjusting airflow based on specific zone requirements. Key components include dampers and airflow sensors that work together to maintain comfort while conserving energy.
Supermarket HVAC Basics Explained – Refrigeration / Ventilation hvac building services
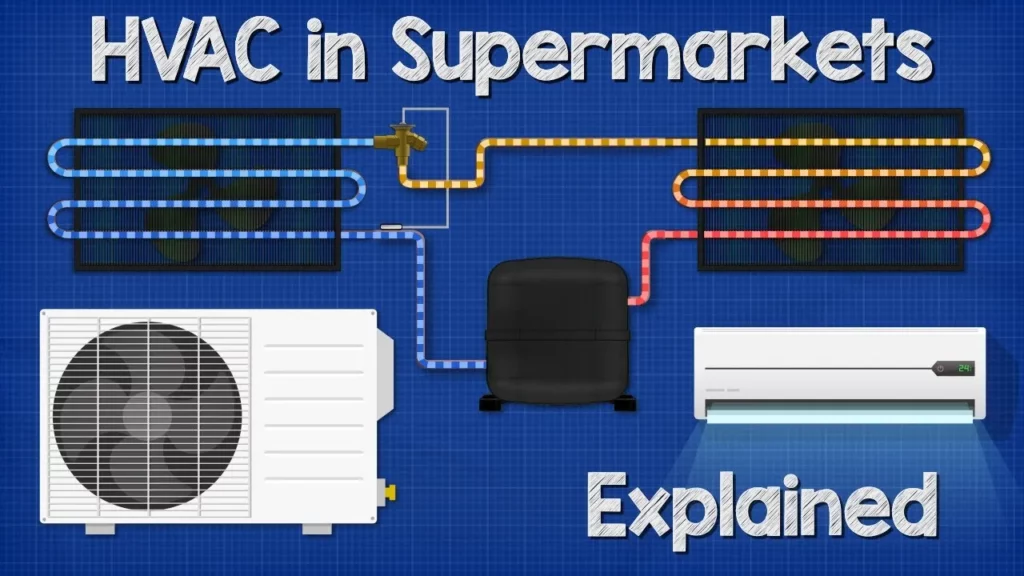
This lesson provides an overview of HVAC systems in supermarkets, focusing on their essential components such as air curtains, ventilation systems, fan coil units, and refrigeration systems. It highlights how these systems work together to maintain indoor air quality, manage odors, and preserve food quality, while also discussing innovative trends like transcritical CO2 systems that enhance efficiency. Overall, the lesson emphasizes the importance of effective HVAC integration for the optimal operation of food retail environments.
How Alternators Work – Automotive Electricity Generator

The lesson explains the function and importance of alternators in automotive electrical systems, detailing how they generate electricity by converting mechanical energy from the engine into alternating current (AC) and then into direct current (DC) for the vehicle’s electrical components. It covers the alternator’s components, including the pulley, stator, and rectifier, as well as the role of the voltage regulator in maintaining consistent output. Overall, understanding the alternator’s operation is essential for appreciating the intricate systems that ensure a vehicle’s functionality.
Transistors Explained – How transistors work

This lesson explains the fundamental workings of transistors, particularly focusing on bipolar transistors, which serve as both switches and amplifiers in electronic circuits. It covers the structure, functionality, and types of bipolar transistors (NPN and PNP), illustrating how a small voltage at the base can control larger currents, akin to regulating water flow in a pipe. Additionally, the lesson highlights the role of semiconductors and the importance of understanding transistor specifications for effective application in technology.
DC Series circuits explained – The basics working principle
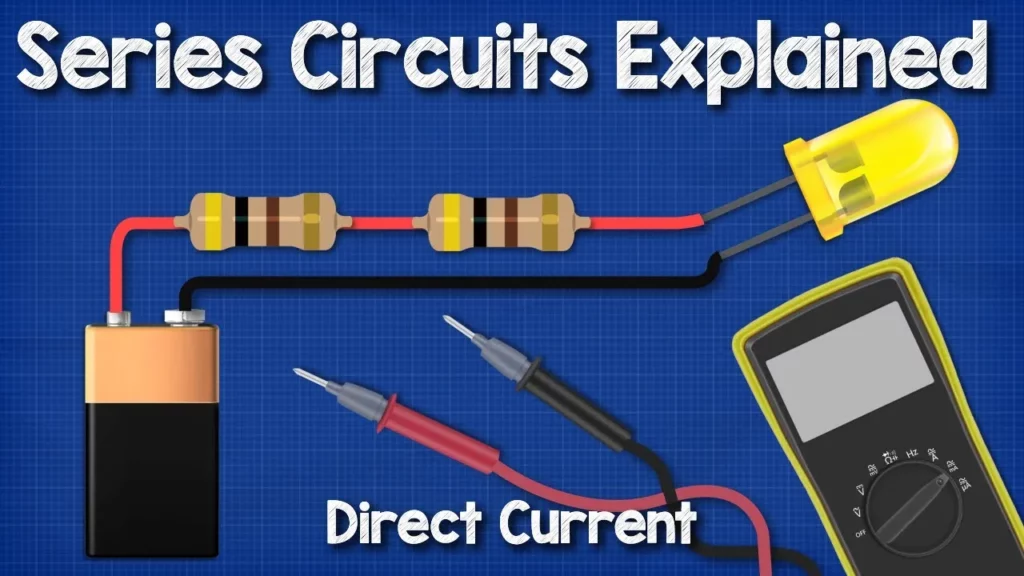
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of DC series circuits, focusing on key concepts such as voltage, current, resistance, and power consumption. It explains how components in a series circuit are connected end-to-end, resulting in a single path for current flow, and details the calculations for total resistance, current, and voltage drops across components. Additionally, the lesson emphasizes the practical application of these principles using a multimeter to measure circuit parameters, reinforcing the importance of understanding these fundamentals for effective circuit design and troubleshooting.
How 3 Phase Power works: why 3 phases?

This lesson explains the fundamentals of three-phase power, highlighting its advantages over single-phase systems. It details how three-phase electricity is generated using a generator with multiple coils, resulting in a more efficient and stable power supply, particularly beneficial for industrial applications. The lesson also covers the configurations of three-phase systems, power distribution, and the global variations in voltage and frequency.
Chiller Basics – How they work
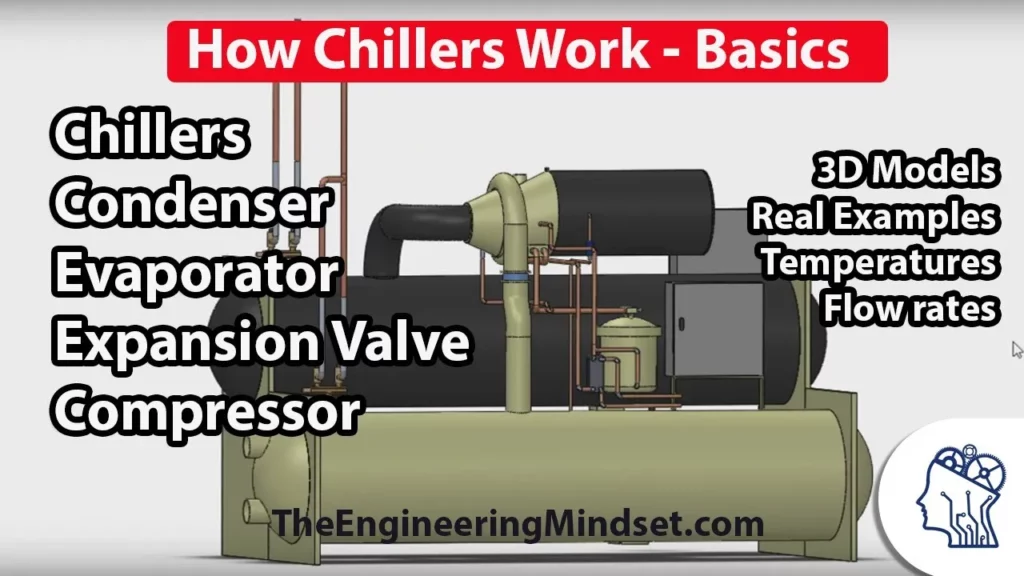
This lesson provides an overview of chillers, essential components of modern air conditioning systems that produce chilled water for cooling buildings. It explains the operational cycle of a chiller, detailing the roles of its four main components—evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve—as well as the three key circuits involved in the process. Additionally, the lesson highlights the importance of understanding different chiller types and their applications in various settings.
This Circuit works without electricity

The lesson introduces the Spintronics game, which allows users to explore mechanical circuits using components like transistors, capacitors, and resistors powered by a mechanical battery. It emphasizes the visualization of electrical concepts through mechanical analogs, demonstrating how current and voltage behave in series and parallel circuits, as well as the functions of capacitors, inductors, transistors, and diodes. The lesson encourages hands-on experimentation and creativity in building circuits, highlighting the educational value of the kit and its accompanying resources.