What is a Servo Motor and What Does It Do?

This lesson provides an overview of servo motors, highlighting their role in converting electrical energy into mechanical energy for precise movement control in various applications, such as robotics and automation. It distinguishes servo motors from standard DC motors by explaining their operation based on specific signals for controlled rotation, and categorizes them into closed-loop and open-loop types, emphasizing the importance of torque ratings, operating voltage, and current considerations. Additionally, the lesson touches on how the physical size of a servo motor correlates with its torque rating and performance.
Thermistor Basics – NTC PTC
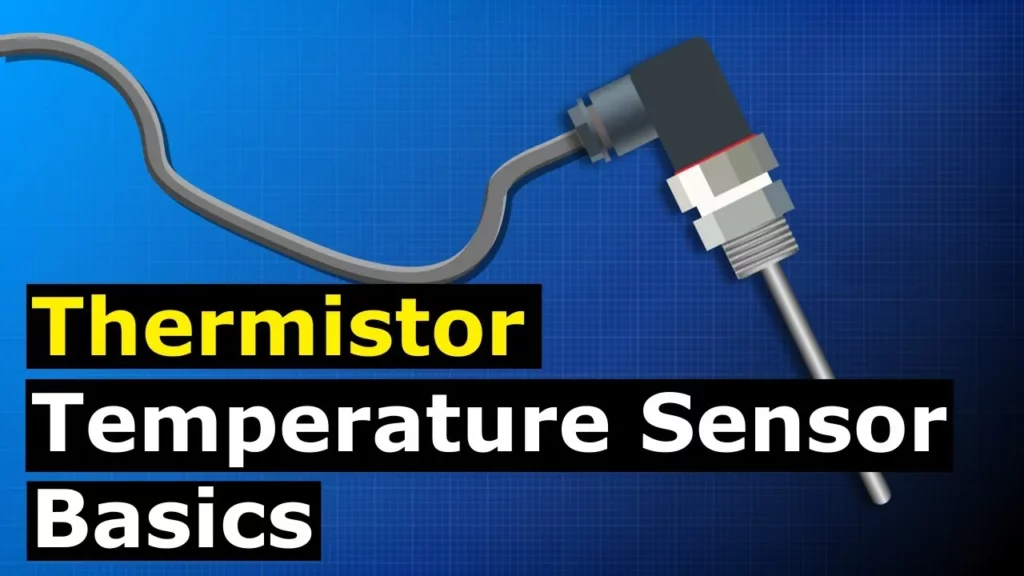
This lesson provides an overview of thermistors, focusing on their function as temperature-sensitive resistors with two main types: Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) and Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC). NTC thermistors decrease in resistance as temperature rises, while PTC thermistors exhibit the opposite behavior. The lesson also explains the underlying science of thermistors, including their construction and the semiconductor properties that enable them to effectively measure and control temperature in various electronic applications.
Pump NPSH Basics

The lesson on Pump NPSH Basics emphasizes the importance of understanding Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) in pump operation, specifically the distinction between Required NPSH (NPSHR) and Available NPSH (NPSHA). It highlights that maintaining NPSHA above NPSHR is crucial to prevent cavitation, a damaging phenomenon that occurs when pressure drops below the liquid’s vapor pressure, potentially leading to significant damage to the pump. Overall, ensuring proper NPSH levels is essential for the efficiency and longevity of pumps.
What is Torque? – Torque basics explained

This lesson introduces the concept of torque, which measures the force that causes an object to rotate around a point. It explains how the length of a wrench affects the torque applied, demonstrating that a longer wrench allows for greater torque, making it easier to turn objects like nuts. Additionally, the lesson discusses the relationship between gears and torque, highlighting how low gears provide high torque for starting and climbing, while high gears offer higher speeds with less torque.
Testing Batteries With a Multimeter – AA Battery Test

In this lesson, we learned how to test AA batteries using a multimeter, a device that measures electrical properties like voltage. By setting the multimeter to measure DC voltage and connecting it to the battery, we can determine if the battery is still functional based on its voltage reading, both under no load and under load with a resistor. A significant drop in voltage during the load test indicates that the battery needs to be replaced.
H Bridge Motor Control Basics Explained
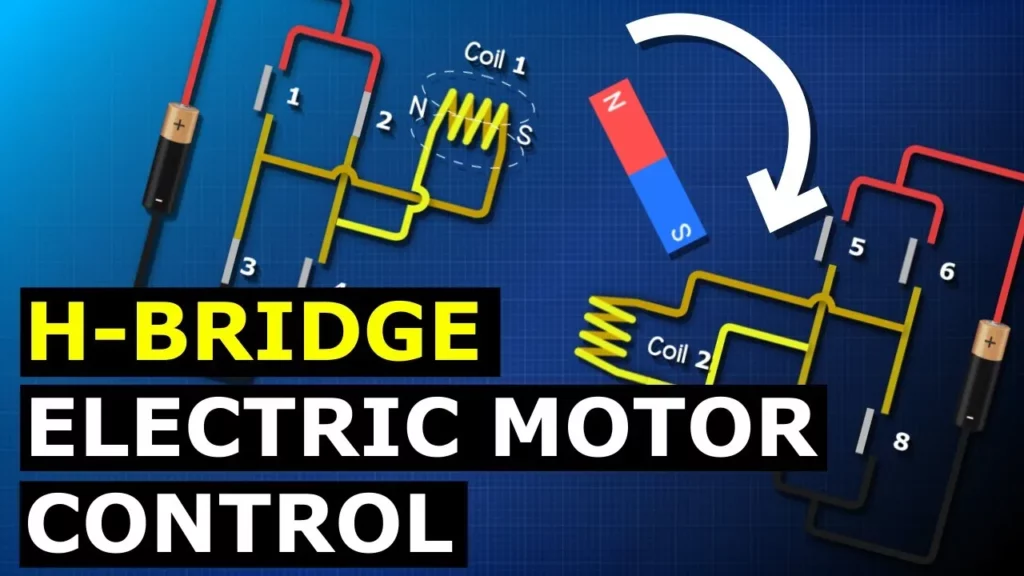
The lesson on H Bridge Motor Control explains how electromagnets can be used to control the movement of a motor by manipulating magnetic fields through an H-bridge circuit. By using electronic switches to alternate the direction of current in coils, the rotor’s movement can be precisely controlled, allowing for both direction and speed adjustments. This foundational understanding of electromagnetism and motor control is essential for applications in electrical and electronics engineering.
Laptop Heat Pipes Explained – how laptop cooling works
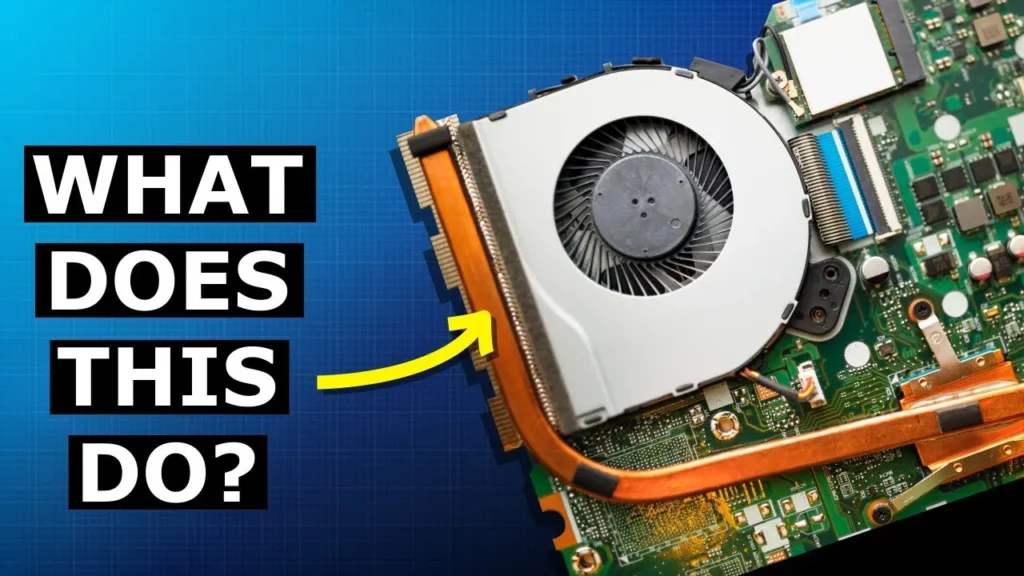
This lesson explains the function of heat pipes in laptops, which are essential for managing heat generated by the processor. Heat pipes utilize a cycle of boiling and condensing liquid to transfer heat away from the processor to a cooler area, aided by a fan. While effective, heat pipes have limitations in terms of size and heat removal capacity, which can impact laptop design and performance.
Why Transformers Use kVA Not kW

This lesson explains why transformers are rated in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) instead of kilowatts (kW), emphasizing the importance of apparent power, which includes both true power and reactive power. Transformers handle a combination of these power types, and using kVA allows for a more comprehensive understanding of their capacity regardless of the specific loads connected. The analogy of beer and foam illustrates the distinction between useful power and wasted power, highlighting the significance of efficiency in electrical systems.
How to build gear set for rear differential 3D print

This lesson teaches you how to build a 3D-printed model of a rear differential, a crucial component that allows cars to turn corners smoothly by enabling the wheels to rotate at different speeds. The process involves assembling various gears and components, ensuring they are securely attached for optimal functionality. By completing this project, you’ll gain hands-on experience and a deeper understanding of how the rear differential operates in vehicles.
What is a resistor? #electronics #electrical #engineering #electricity

In this lesson, we learned that resistors are crucial components in electronic circuits that help control the flow of electricity, preventing overheating and damage to sensitive parts like LEDs. They function by creating resistance, which slows down the movement of electrons, much like a traffic cop managing cars on a highway. Choosing the right resistor is essential for ensuring that circuits operate safely and efficiently.