How SpaceX Will Test 29 Raptor Engines

In preparation for the first orbital launch of the Starship, SpaceX is set to conduct a critical static fire test of all 29 Raptor engines on the Super Heavy booster, Booster 4. This test follows several pressure tests and aims to ensure the engines function flawlessly, with a focus on managing the immense thrust and potential risks associated with firing multiple engines simultaneously. By employing advanced technology and innovative launch pad designs, SpaceX hopes to overcome challenges faced by previous rocket programs and successfully pave the way for their historic launch.
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 Identity Problem

The lesson discusses the journey of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 upper stage, which, after launching a climate observation satellite in 2015, was predicted to crash into the Moon after seven years in space. Initially identified as space debris from the Falcon 9, further analysis revealed it was likely part of China’s Chang’e 5 mission, highlighting the complexities of tracking and identifying objects in space. The lesson emphasizes the importance of precise predictions in space exploration and the potential for future discoveries of such debris as human presence on the Moon increases.
SpaceX’s Abandoned Starship Factory

The lesson discusses SpaceX’s development of the Starship rocket, focusing on the competition between its Boca Chica, Texas, site and a smaller facility in Cocoa, Florida. While Boca Chica’s expansive area allowed for more efficient construction and experimentation, the Cocoa site faced logistical challenges that ultimately led to its closure, with resources being redirected to Boca Chica. Despite this, the Cocoa site continues to play a role in manufacturing components for Starship, and plans for a new facility near Kennedy Space Center are underway to enhance operations.
How SpaceX Mastered Starship’s Welding

The lesson on SpaceX’s Starship highlights the significant advancements in design and welding techniques that transformed the spacecraft from its rough early prototypes to a more sophisticated and robust vehicle. Initially intended to be made from carbon fiber, SpaceX pivoted to stainless steel for its superior heat resistance and cost-effectiveness, while overcoming early welding challenges through improved methods and automation. The evolution of welding techniques, including the adoption of TIP-TIG and laser welding, has not only enhanced the structural integrity of Starship but also contributed to its refined appearance, showcasing SpaceX’s commitment to innovation and rapid development in aerospace technology.
Why Starlink’s In-flight WiFi is a Game Changer

The lesson discusses how Starlink’s satellite internet service from SpaceX is set to transform in-flight WiFi by providing faster speeds and lower latency compared to traditional air-to-ground systems. By utilizing a network of satellites closer to Earth, Starlink can enhance bandwidth availability for passengers and enable real-time data transmission for airlines, potentially improving safety and operational efficiency. Despite regulatory and cost challenges, the future of in-flight connectivity looks promising with Starlink’s advancements.
SpaceX’s Genius New Starlink Technique
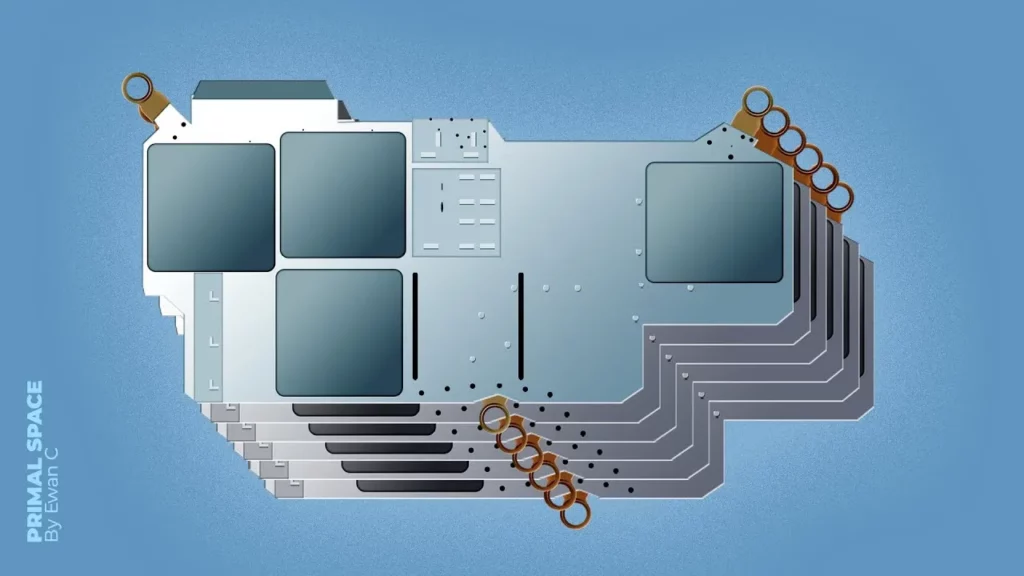
SpaceX is advancing its Starlink satellite deployment strategy through the innovative design of its Starship prototype, SN24, which features a specialized cargo bay door for launching larger satellites that cannot be accommodated by the Falcon 9 rocket. The company has developed a unique mechanism for satellite deployment, inspired by industrial systems, to address the challenges of microgravity in orbit. As SpaceX prepares for upcoming launches, their commitment to enhancing satellite deployment efficiency and infrastructure signals a promising future for their space operations.
Transporting the James Webb Telescope: How They Moved the World’s Most Valuable Object

The lesson details the remarkable journey of the James Webb Telescope, which launched on December 25, 2021, after overcoming numerous challenges and delays since its inception in 1996. It highlights the meticulous planning and execution involved in transporting the telescope safely from its assembly location to the launch site, including the creation of a specialized shipping container and a carefully coordinated route to minimize disruption. The collaborative effort behind the telescope’s development and its anticipated contributions to our understanding of the universe are also emphasized.
SpaceX’s 80 Year Old Factory

The lesson explores the historical significance of SpaceX’s McGregor testing facility, tracing its origins from a World War II bomb factory to a pivotal site for rocket engine development. Since SpaceX’s acquisition in 2003, McGregor has played a crucial role in testing engines for the Falcon 9 and the Raptor engine for the Starship, expanding significantly to meet the demands of modern space exploration. As SpaceX aims for ambitious goals like sending humans to Mars, McGregor’s contributions to engine testing and production remain vital to the company’s success.
SpaceX’s Critical Super Heavy Decision

The lesson discusses SpaceX’s journey in mastering rocket landings, highlighting their initial challenges with the Falcon 9 and their subsequent success in achieving over 128 successful landings. It also focuses on the upcoming Starship program and the critical decision regarding whether to attempt to catch the Super Heavy booster on its first flight, emphasizing the risks and potential rewards of such a bold move. Ultimately, the lesson underscores SpaceX’s innovative spirit and willingness to take risks in pursuit of advancements in space exploration.
What Happens When Russia Leaves The ISS?
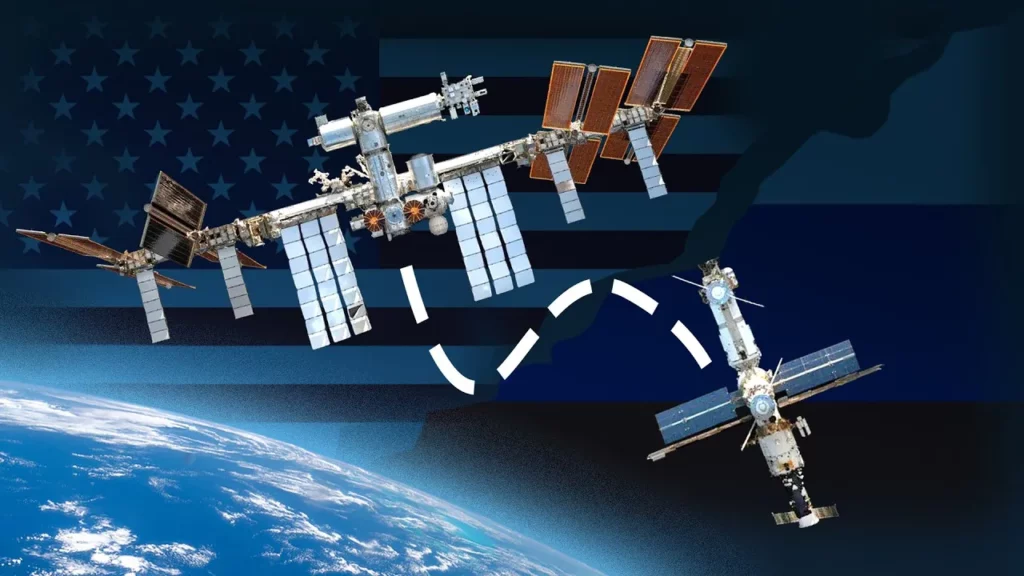
The lesson discusses the implications of Russia’s decision to leave the International Space Station (ISS) after 2024, highlighting the historical collaboration that led to the ISS’s creation and its current technological challenges due to aging infrastructure. Russia’s departure could jeopardize the ISS’s operational stability, particularly its ability to maintain orbit, while also paving the way for Russia to develop its own space station, ‘Ross,’ by 2028. The lesson emphasizes the importance of continued international cooperation in space exploration, despite potential shifts in partnerships.