New Lessons
AI Essay Grader
Essay Grader Revolutionizing Academic Assessments Faster, Fairer, and Accurate Legacy Grader My Graded Essays Premium Grader Result List/Edit Graded Essays Dynamic.ooo – …
AI Essay-Writing Guide – High School
AI Essay-Writing Guide – High School A few important things to keep in mind: Have your notebook and pen ready. Jot down …
AI Essay-Writing Guide – Elementary School
AI Essay-Writing Guide – Elementary School Important things to remember: Have a pencil and notebook ready. First, write in your notebook before …
Intermediate Conversations: Advanced Presentation and Public Speaking Skills
Advanced Presentation and Public Speaking Skills - Chat with your AI teacher. The topic is Advanced Presentation and Public Speaking Skills. Practice and improve your English skills with AI conversations on ClassX.
AI Essay-Writing Guide – Elementary School 2
AI essay writing guide for elementary school students. Important things to remember: Have a pencil and notebook ready. First, write in your …
Refrigeration Design Software – Coolselector®2 HVACR
This lesson introduces Coolselector 2, a free refrigeration design software developed by Danfoss, aimed at HVAC refrigeration engineers and students. The software simplifies the selection of refrigeration components, offering features such as system schematics, performance analysis, and report generation, while also providing practical applications for selecting components like thermostatic expansion valves and compressors. Additionally, users can customize their experience and access extensive training resources to enhance their understanding of refrigeration design.
AFCI Breaker Basics – Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter how they work
The lesson on Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) highlights their crucial role in preventing electrical fires by detecting and interrupting arc faults caused by damaged insulation. AFCIs are mandated by the National Electric Code for specific residential areas and operate by monitoring electrical currents for dangerous patterns, automatically tripping to cut off power when an arc is detected. Understanding AFCIs is vital for maintaining electrical safety in homes and ensuring proper installation and operation.
Learn the Basics of HVACR Time Control
The lesson on HVACR time control emphasizes its importance in optimizing energy efficiency and comfort by allowing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to operate only when necessary. It explains the evolution from traditional mechanical timers to modern electronic controllers, which offer advanced scheduling features and adaptability for various settings, including larger buildings that utilize programmable logic controllers for precise temperature management. Additionally, the lesson encourages further exploration of HVAC engineering through various educational resources and social media platforms.
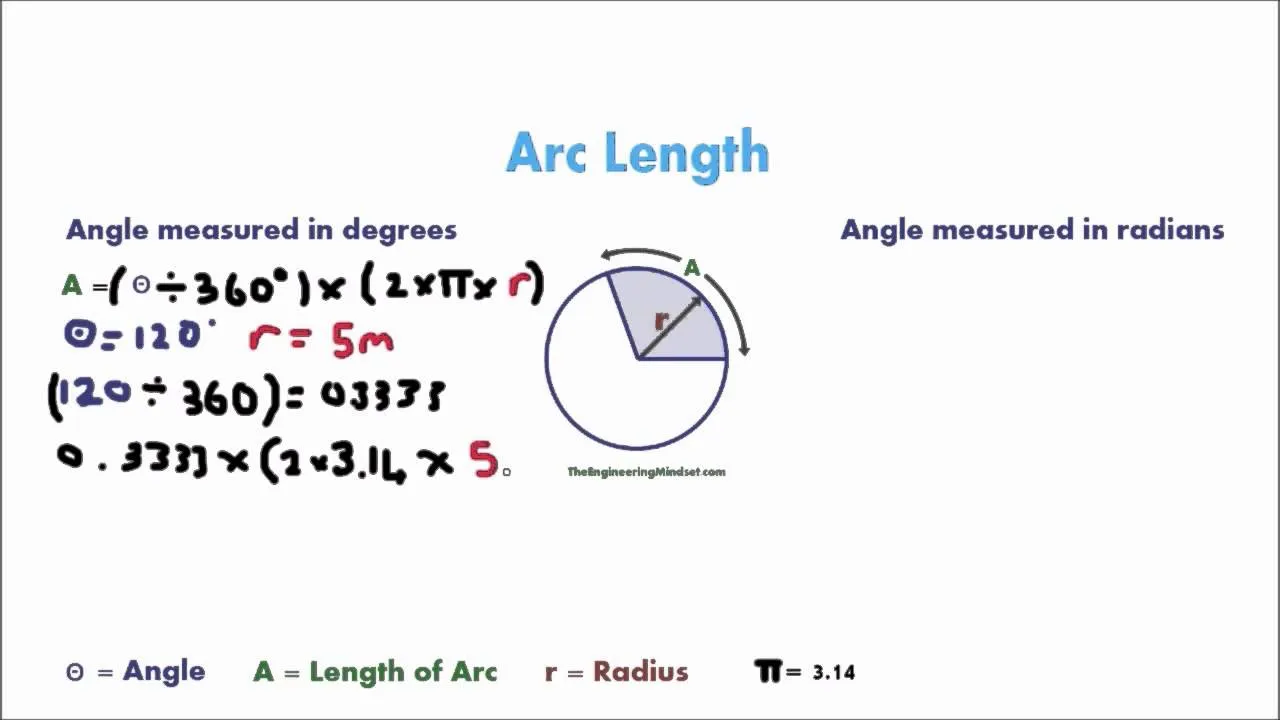
Arc length, degrees & radians tutorial with example
In this lesson, we learned how to calculate the length of an arc in a circle using two methods: one for angles in degrees and another for angles in radians. The formula for degrees involves taking the ratio of the angle to 360° and multiplying it by the circle's circumference, while the formula for radians is simply the angle multiplied by the radius. With practice, these calculations can become straightforward and intuitive!
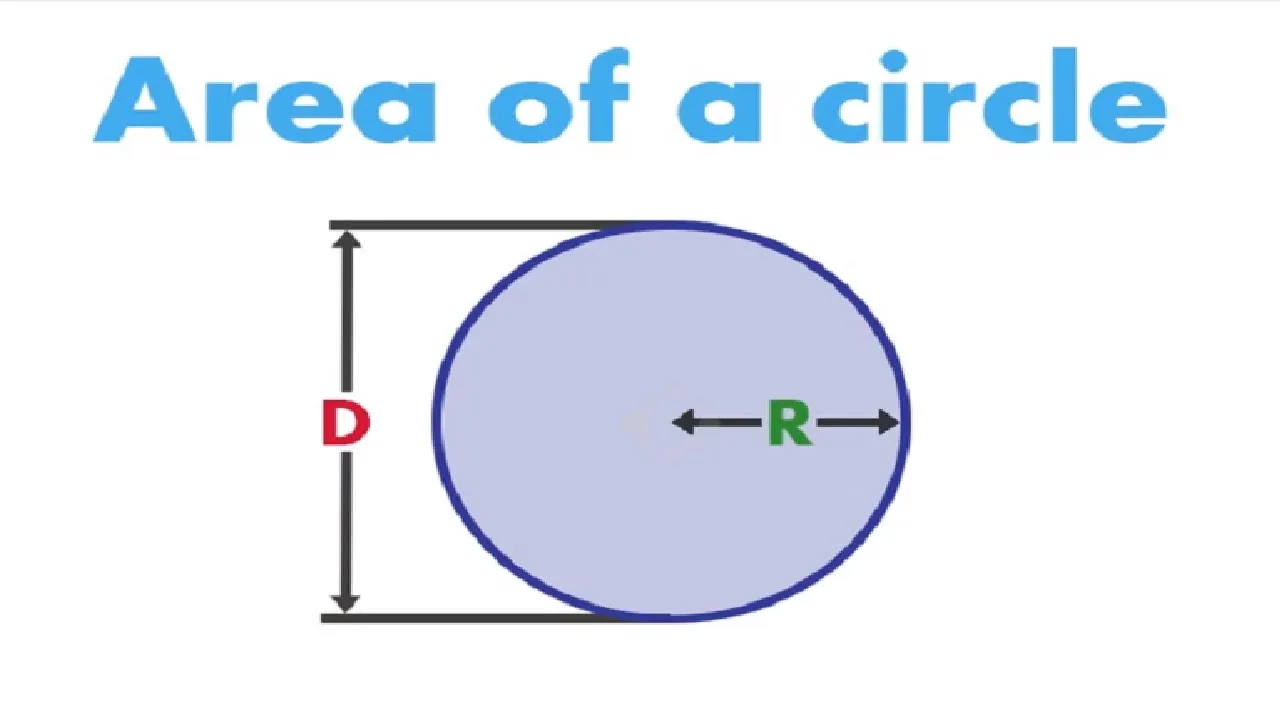
Calculate the Area of a circle from Radius or Diameter
In this lesson, you learned how to calculate the area of a circle using either the radius or the diameter. By applying the formulas Area = π × radius² or Area = (π × diameter²) / 4, you can easily find the area of a circle, with both methods yielding the same result. With practice, you'll become proficient in determining the area of circles quickly and accurately.
HVAC On Off Control Basics
This lesson explains the fundamentals of on/off control in HVAC systems, highlighting how simple switches and thermostats regulate heating and cooling. It describes the operation of a thermostat using a bi-metallic strip to maintain a comfortable temperature automatically, while also addressing the importance of manual overrides for personal comfort. Additionally, the lesson emphasizes the need for shorter on/off intervals to achieve more consistent temperature control in spaces that require less heating or cooling.
The lesson addresses the pressing global issue of drinking water scarcity and explores innovative solutions, particularly the conversion of seawater into freshwater through desalination technologies like Danfoss's iSave system. It highlights the critical need for water in daily life and agriculture, the challenges faced by major cities experiencing severe shortages, and the mechanics of reverse osmosis as an effective purification method. The iSave technology enhances energy efficiency in the desalination process, significantly reducing energy consumption while ensuring the quality of the purified water.
Heating System Optimizer Basics
This lesson focuses on the role of electronic controllers in managing heating systems in modern buildings, highlighting their ability to set customizable schedules for efficient operation. It explains how advanced systems with optimizers, integrated with programmable logic controllers (PLCs), enhance heating efficiency by adjusting activation times based on occupancy and temperature conditions. Additionally, the lesson encourages further exploration of HVAC engineering through educational resources and social media platforms.
Refrigeration Design Software – Coolselector 2
The lesson introduces Coolselector 2, a user-friendly refrigeration design software by Danfoss, which allows HVAC professionals and students to efficiently design and optimize refrigeration systems. It features built-in wizards for tasks like cold room design, offers comprehensive design data and reports, and supports various applications, making it a valuable tool for assessing component compatibility and performance. The software is free to download, and Danfoss also provides additional resources on natural refrigerants and industry regulations.
10 Engineering projects Tackling Ocean Pollution #TeamSeas
The lesson highlights innovative engineering projects aimed at combating ocean pollution, spearheaded by organizations like TeamSeas.org, which seeks to remove 30 million pounds of trash from waterways. Various creative solutions are presented, including robots like Waste Shark and ClearBot, artificial coastlines, and technologies like the Bubble Barrier and Interceptor, all designed to efficiently collect and manage ocean waste. The lesson emphasizes the importance of collective action and encourages individuals to contribute to these initiatives.
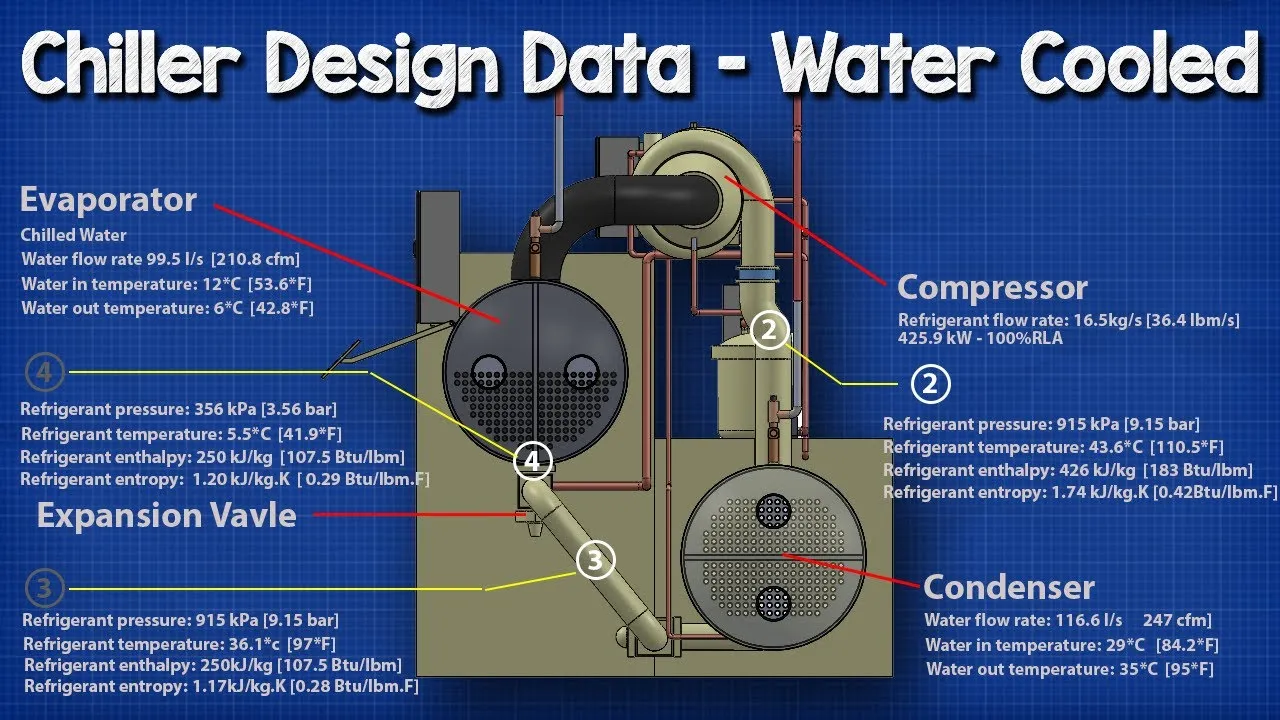
How Chiller works – Design Data
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of centrifugal chillers, focusing on their design, operation, and key components, including the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. It explains the thermodynamic cycle of a centrifugal chiller using a pressure-enthalpy chart, detailing the changes in pressure, temperature, and enthalpy throughout the refrigerant's journey. Understanding these concepts is crucial for optimizing HVAC systems and assessing chiller efficiency and performance.
Fan & motor CALCULATIONS, Pulley size, RPM, air flow rate cfm hvac rtu
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of fan and motor calculations essential for HVAC systems, focusing on determining pulley sizes, RPM, and airflow rates. It outlines key formulas for calculating fan and motor pulley diameters, as well as how to adjust these parameters to optimize system performance and energy efficiency. By mastering these calculations, you can effectively design or modify HVAC systems to ensure they operate efficiently and meet specific airflow requirements.
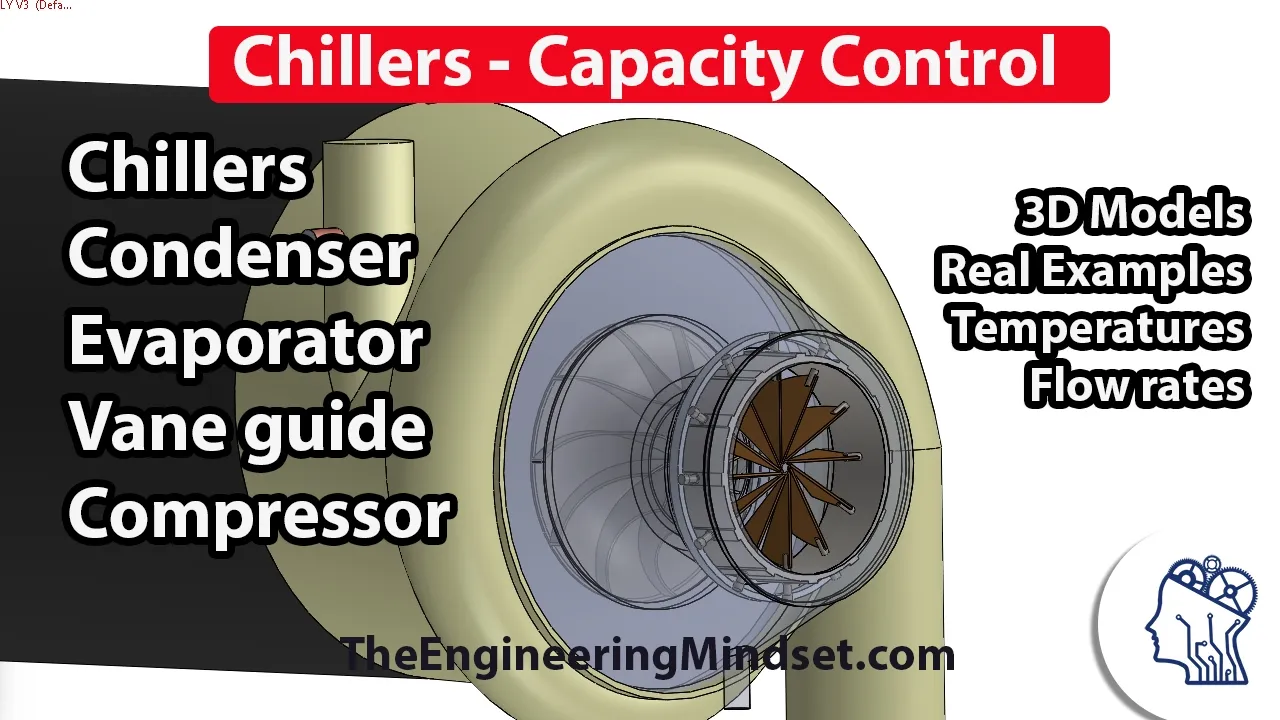
Chiller – Cooling Capacity Control
This lesson focuses on chiller capacity control, specifically examining the role of vane guides in centrifugal chillers. Vane guides are crucial for regulating refrigerant flow and maintaining the desired chilled water temperature, which is essential for efficient cooling operations in buildings. By adjusting the angle of the vanes, the system can optimize refrigerant flow and energy use, ensuring that the chiller operates effectively across varying capacities.
Why Are Solenoid Valves Used?
Solenoid valves are crucial for remotely and automatically controlling the flow of various fluids in systems, enhancing efficiency and safety without manual intervention. They are widely used in applications ranging from household appliances to industrial and HVAC systems, such as managing cooling in refrigeration and controlling fluid flow in manufacturing processes. Their versatility allows for precise control in critical operations, making them an essential component in modern engineering.
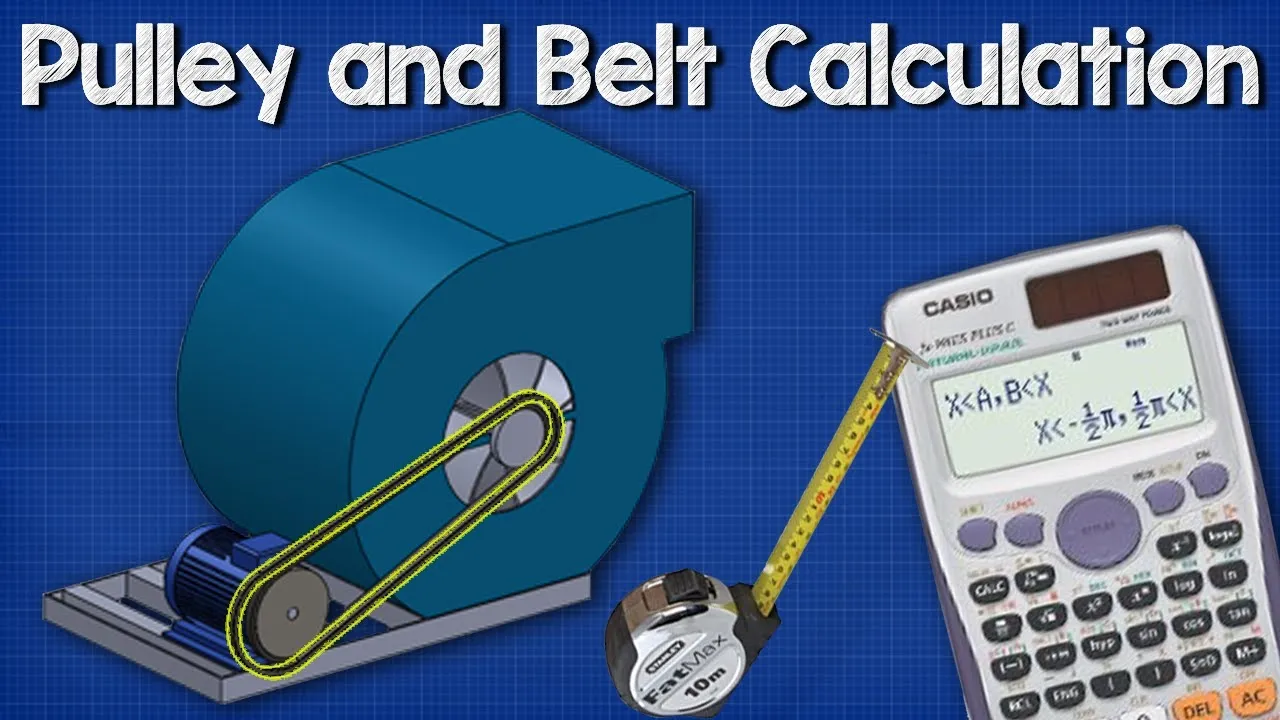
Pulley Belt CALCULATIONS – Belt length, distance between pulley wheels
This lesson focuses on the essential calculations for determining belt length and the distance between pulleys in a pulley system, which is vital for various industrial applications like air handling units and conveyor belts. By understanding the sizes of the pulleys and the center-to-center distance, learners can accurately calculate the belt length and center distance, facilitating efficient design and maintenance of pulley systems. Utilizing tools like spreadsheet software can further streamline these calculations, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency.
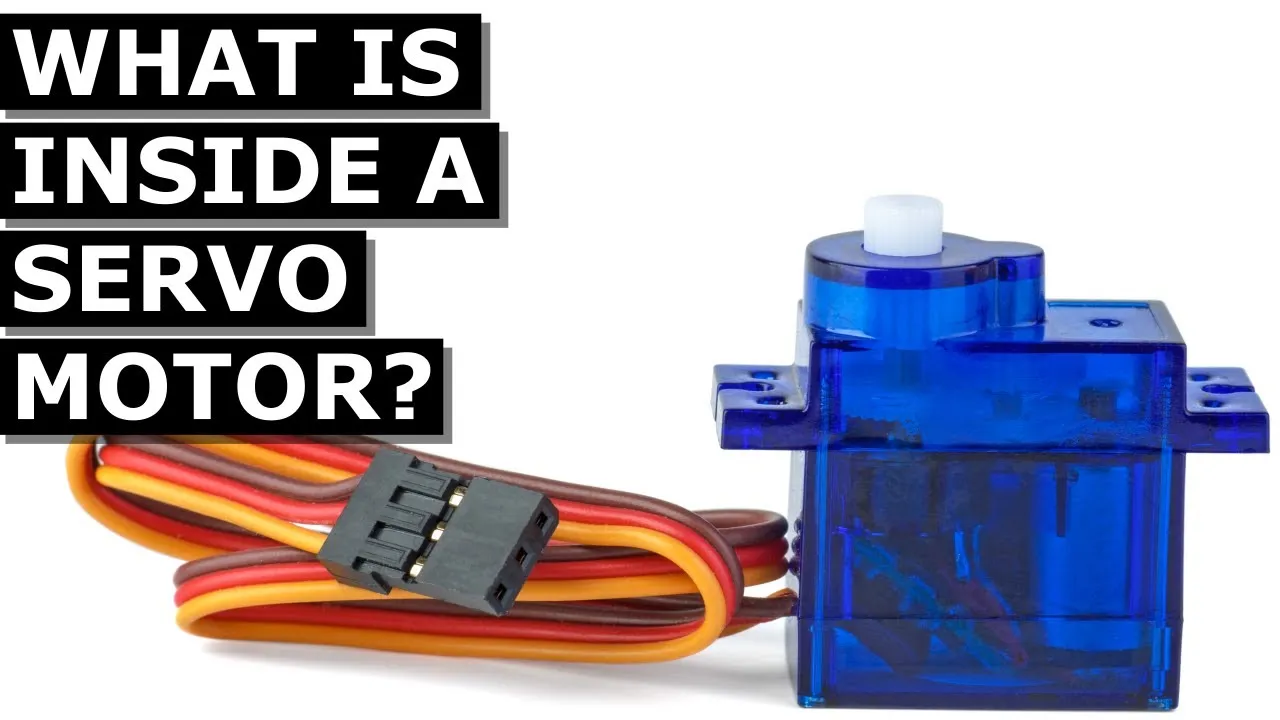
Servo Motor, what's inside?
The lesson explores the inner workings of a servo motor, detailing its components such as the housing, gears, circuit board, and potentiometer. It explains how the motor converts high-speed, low-torque input into low-speed, high-torque output, and how it uses PWM signals to determine its position through feedback from the potentiometer. Overall, the lesson provides a comprehensive overview of how servo motors operate and are controlled.
Cooling Load Calculation – Cold Room hvac
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of calculating the cooling load for a cold room, which is essential for maintaining the quality of perishable goods. It outlines the various sources of heat that must be accounted for, including transmission loads, product loads, internal loads, equipment loads, and air infiltration. By performing sample calculations and applying a safety factor, the lesson guides readers in determining the appropriate refrigeration unit size to effectively manage the cooling load.
Pump CALCULATIONS, Flow rate, RPM, Pressure, Power, Diameter
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of essential pump calculations, including flow rate, RPM, head pressure, power, and impeller diameter. It offers formulas to help users determine how changes in RPM and impeller size affect pump performance, enabling better understanding and prediction of pump behavior for both existing and new installations. The guide emphasizes the importance of using accurate data and adjusting parameters to optimize pump efficiency.
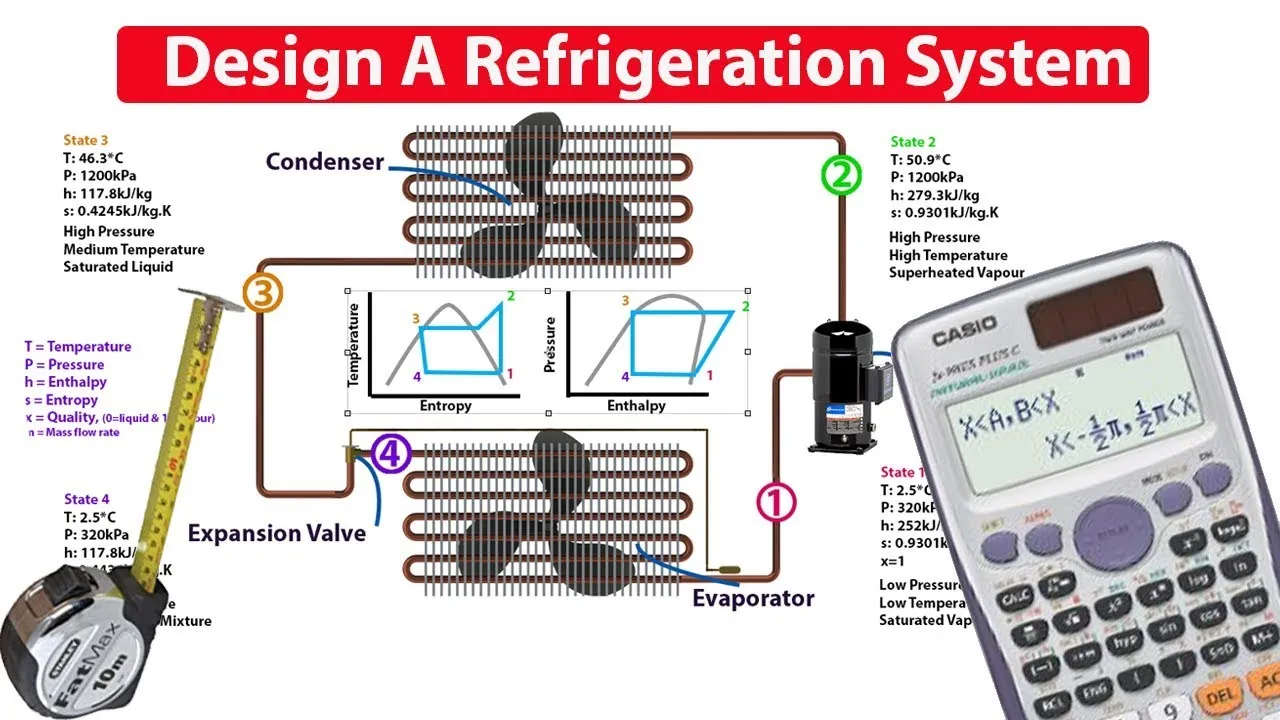
How to DESIGN and ANALYSE a refrigeration system
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of designing and analyzing refrigeration systems, focusing on the ideal vapor compression cycle and its four main components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. It emphasizes the importance of understanding key thermodynamic properties at various points in the cycle, using refrigerant R134a as an example, and highlights how to calculate system performance through the coefficient of performance (COP). The lesson encourages starting with the desired cooling load to optimize system efficiency and performance.