Grade 8 Video Lessons
Elevate your learning with our AI-guided video lessons, designed for Grade 8 students! We've curated engaging YouTube videos to make learning more exciting and thought-provoking.
The Sahara Desert receives an abundance of solar energy, raising the possibility of covering it with solar panels to solve global energy problems. However, there are limitations to solar panel efficiency and challenges associated with large-scale solar farms, such as heat absorption and environmental impact. Alternative solutions, such as concentrated solar power plants using giant mirrors, are being explored. Additionally, solar energy can exist on smaller scales, providing a passive source of energy for individual buildings and rural communities.
The article discusses the concept of flow, which is a unique mental state of effortless engagement in a task. Flow is associated with positive emotions, creativity, and feelings of accomplishment, as well as increased productivity and learning. The article also explores unanswered questions about flow and provides tips on how to increase the chances of experiencing flow.
The article debunks common myths and misconceptions about medieval Europe. It explains that medieval people were not ignorant or uneducated, they had methods for preserving food and practiced hygiene, and many supposedly medieval torture devices were actually more recent inventions. The article also discusses how perceptions of the Middle Ages have varied throughout history.
Scientists believe that daydreaming serves a purpose and is not a waste of time, as we spend between a third and half of our waking hours daydreaming. Daydreaming activates different brain areas, known as the default mode network, which is associated with rest, memory recall, future planning, and creative thinking. The interplay between the default mode network and the executive network, responsible for logical thinking, is crucial for creative thinking and problem-solving.
The article discusses the physics behind Roberto Carlos's famous free kick during a 1997 match, highlighting the role of the Magnus effect in the ball's dramatic curve. By striking the ball with a specific spin, Carlos created a pressure differential that caused the ball to swerve unexpectedly into the goal, exemplifying the complexity and beauty of executing a banana kick in soccer. The piece also touches on the Magnus effect's application in various sports and the theoretical limits of achieving extreme ball curves.
Frida Kahlo's life was profoundly shaped by a tragic bus accident in 1925, which led her to discover painting as a means of therapy and self-expression. Her art, characterized by vibrant colors and deep symbolism, often reflected her physical pain, tumultuous relationships, and rich Mexican heritage, particularly through her iconic self-portraits. Despite her passing in 1954, Kahlo's legacy continues to resonate, as her work offers complex insights into her identity and experiences, solidifying her status as a significant figure in the art world.
The article recounts the tragic fate of Rome's Vestal Virgins, focusing on the harrowing experience of a priestess condemned to live burial for alleged unchastity, highlighting the severe consequences of their sacred duties. It follows young Licinia, who is chosen to become a Vestal Virgin, as she undergoes rigorous training to maintain the sacred flame of Vesta, a symbol of Rome's endurance. The narrative underscores the immense pressure and fear these women faced, as their lives were intricately linked to the city's fortunes and the ever-present threat of sacrifice for perceived failures.
In the lesson "Cracking the Code: The Art of the Perfect Heist at the Fabergé Egg Museum," a jewel thief devises a strategic plan to determine the highest floor from which a Fabergé egg can be dropped without breaking, using two replica eggs for testing. By employing a method that optimizes the number of attempts through calculated intervals, she concludes that starting from the 14th floor allows her to identify the critical floor in a maximum of 14 drops. This lesson emphasizes the importance of precision and strategic planning in executing a successful heist.
In "The Hardest Logic Puzzle: Deciphering Alien Overlords," participants must navigate a complex riddle involving three alien overlords—Tee, Eff, and Arr—who provide answers that are either always true, always false, or random. The challenge lies in formulating three strategic yes-or-no questions to identify each overlord, despite not knowing which of the two words means yes or no. By embedding hypothetical scenarios into their questions, participants can derive useful information regardless of the truthfulness of the answers, ultimately leading to the successful identification of the aliens and escape from the planet.
The lesson explores the ancient origins of cheese, tracing its development from Neolithic farmers in the Fertile Crescent around 8000 BCE to its integral role in various ancient civilizations. It highlights how cheese provided nutritional benefits and survival advantages, evolving through cultural adaptations and technological advancements, ultimately leading to the modern cheese industry that produces billions of kilograms annually while still honoring traditional methods.
The lesson explores the rise of the Sumerian civilization, recognized as the world's first empire, which emerged in the challenging environment of Mesopotamia around 5000 BCE. Through innovations in agriculture, urban development, and trade, the Sumerians established city-states characterized by complex social structures, monumental architecture, and the invention of writing. Despite their eventual decline due to invasions, Sumer's cultural and technological contributions significantly influenced subsequent civilizations, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate in modern society.
In "The Epic Tale of Väinämöinen and the Quest for the Sampo," the legendary bard Väinämöinen embarks on a perilous journey to create and reclaim the mythical Sampo, an artifact that promises endless wealth. After persuading the skilled smith Ilmarinen to forge the Sampo in the icy realm of Pohjola, they successfully create it, but their triumph is short-lived as they face Louhi's wrath in a final battle. Ultimately, the Sampo is lost to the sea, its remnants now serving a different purpose under the watch of Ahti, the god of water.
The lesson on the respiratory system highlights the pathway of air from the trachea to the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled. It discusses pneumonia, an infection that disrupts this gas exchange by filling the alveoli with fluid, and outlines the body's defense mechanisms, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures against pneumonia, emphasizing the importance of a healthy lifestyle and vaccinations.
The lesson explores the gondola's significance as a symbol of Venice, tracing its historical evolution from a vital mode of transport in the 1500s to a status symbol for the wealthy. It highlights the craftsmanship involved in gondola construction, the impact of regulations on their appearance, and the decline of traditional gondola-making in the face of modernization. Despite the reduction in the number of gondolas, the legacy of this unique craft continues to be celebrated in Venice.
The lesson explores the phenomenon of earworms, which are involuntary snippets of music that frequently intrude into our thoughts, affecting over 90% of people weekly. It delves into the psychological nature of earworms, their repetitive characteristics, and the role of modern technology in their prevalence, while also examining why music, rather than other sensory experiences, tends to stick in our minds. Despite various theories, the exact reasons behind earworms remain a mystery, highlighting the complexities of human cognition.
The lesson of "The Mythical Tale of Ix Chel: The Moon Goddess" explores the rich narrative of Ix Chel, a symbol of love, resilience, and transformation within Maya mythology. Her journey, marked by encounters with the sun god Kinich Ahau and challenges from her protective grandfather, illustrates themes of devotion, betrayal, and self-discovery, ultimately leading her to embrace her identity as a guiding force in the night sky. Ix Chel's legacy reflects the cultural values of the Maya people and highlights the enduring power of myth in shaping identity and inspiration.
The lesson explores the concept of the analemma, a figure-eight pattern formed by the sun's path in the sky when observed from a fixed point over a year. This intriguing shape results from the Earth's axial tilt and its elliptical orbit around the sun, which affects the timing of solar noon and leads to variations in solar declination throughout the seasons. Additionally, the analemma serves as a historical tool for understanding timekeeping, illustrating the complex relationship between Earth's movements and its position relative to the sun.
The lesson "Exploring the Mysteries of the Deep Sea" takes students on a journey through the various zones of the ocean, highlighting the unique adaptations and survival strategies of marine life in extreme environments. From the sunlit surface teeming with phytoplankton to the dark, pressure-filled depths where bioluminescence and teamwork are crucial for survival, the lesson emphasizes the importance of ocean preservation and the mysteries that remain to be uncovered. Ultimately, it calls for a greater understanding and protection of these vital ecosystems for future generations.
The lesson on the measles virus highlights its infectious nature, the immune response it triggers, and the severe complications that can arise from infection. It emphasizes the critical importance of vaccination, not only for individual protection but also for community immunity, as unvaccinated individuals pose a risk to vulnerable populations. Ultimately, the lesson advocates for collective responsibility in eradicating measles through widespread vaccination efforts.
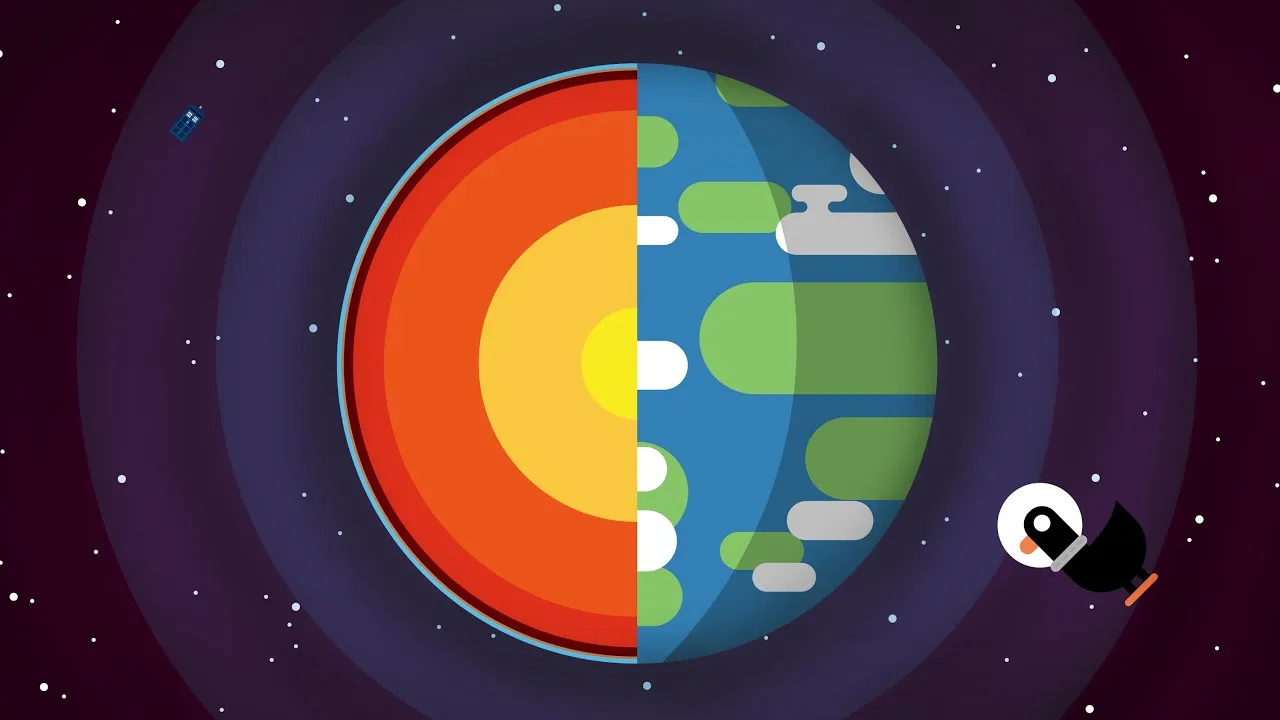
The lesson explores the fascinating formation and structure of Planet Earth, detailing its origins approximately 4.6 billion years ago from a gas cloud of dead stars and the subsequent processes that shaped its surface and atmosphere. It highlights the dynamic nature of Earth's crust due to plate tectonics, the composition of its layers, the significance of its magnetic field, and the protective role of the atmosphere, ultimately emphasizing the rarity and beauty of our planet in the vast universe.
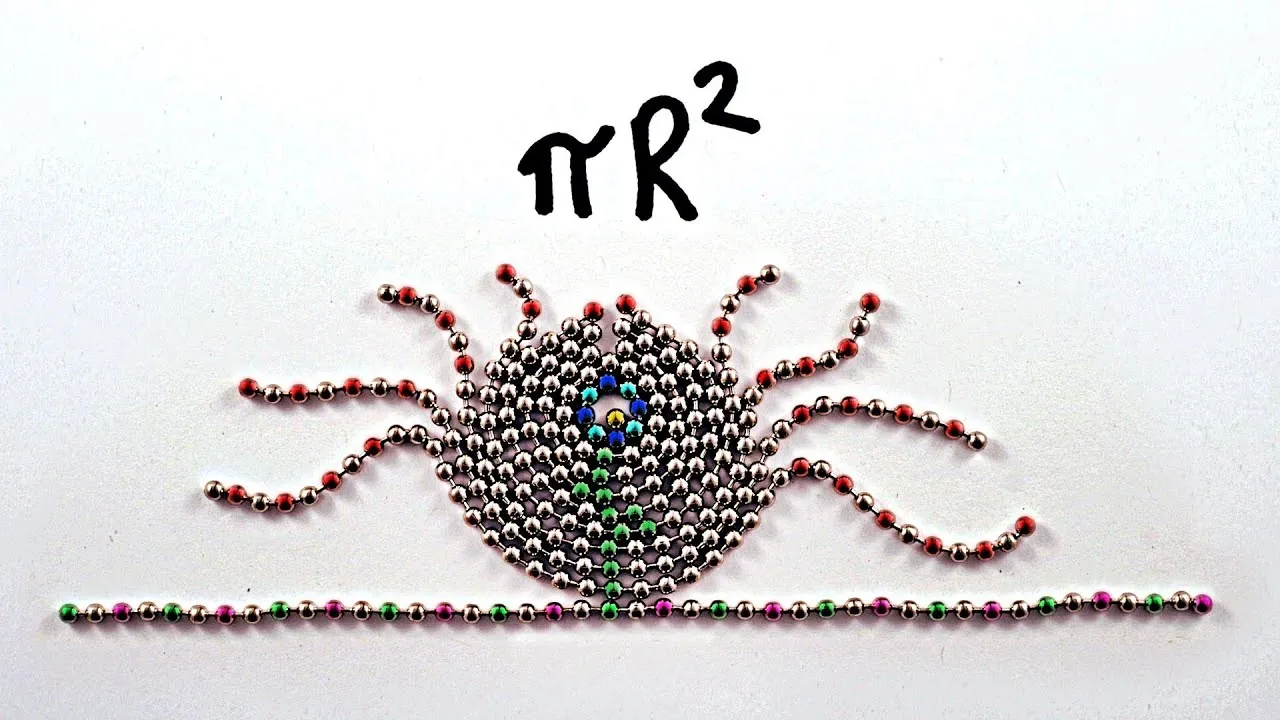
In this lesson, students learn to discover the area of a circle through a fun and visual proof using a chain and a ruler. By measuring the circumference with the chain and rearranging the circle into a rectangle, they can understand that the area of the circle is calculated using the formula Area = π × radius², illustrating the relationship between the circle's radius and circumference. This hands-on approach enhances comprehension of geometric concepts and allows students to share their newfound knowledge with others.
The lesson explores the fascinating engineering behind cruise ships, particularly focusing on the Symphony of the Seas, the world's largest cruise ship. It explains how these massive vessels remain stable and buoyant through their wide hull design, low center of gravity, and advanced stability features, allowing them to handle rough seas and large passenger loads without tipping over. Additionally, the lesson highlights the safety measures taken by cruise ships to navigate bad weather and assist others in distress at sea.
The lesson explores the myth that people swallow spiders while sleeping, specifically focusing on the Sydney funnel-web spider, one of the world's most venomous spiders. It clarifies that while swallowing a spider is unpleasant, the real danger lies in being bitten during the process, as the venom can affect the nervous system; however, if swallowed, the venom is neutralized by stomach acid. Ultimately, the lesson emphasizes that the idea of swallowing spiders is largely a myth and encourages safe practices.
In this thrilling adventure lesson, participants embark on a daring mission to steal a diamond from a secret island, navigating a series of challenges that test their problem-solving and decision-making skills. The journey involves clever escapes, encounters with danger, and the need for quick thinking, ultimately leading to a final test of bravery and resourcefulness. By the end, adventurers receive a score reflecting their performance, encouraging self-reflection on their skills and readiness for future escapades.