Grade 9 Video Lessons
Advance your education with our AI-guided video lessons, crafted for Grade 9 students! We've selected insightful YouTube videos to make learning more engaging and stimulating.
The menstrual cycle is a natural process experienced by all women, lasting between two to seven days every month and occurring approximately 450 times in a woman's life. It is regulated by a series of hormonal controls and involves the ovaries, which release an egg each month, waiting for fertilization by a sperm cell. If fertilization does not occur, the womb's lining degenerates, and the period begins, taking up to a week to clear out the unused contents of the womb, after which the cycle begins again.
Scientists are able to create the coldest materials in the world in physics labs by using laser beams to slow down moving particles. This allows for a better understanding of the inner workings of matter and the development of sensitive instruments, such as atomic clocks and detectors for underground resources. Cold atoms also have the potential to be used in the study of atomic and subatomic phenomena and the detection of gravitational waves.
The article discusses the invisible signals that surround us, such as radio waves, and their impact on various technologies. It explains how airplane mode on phones is not just for protecting flights, but also to prevent interference with other signals. The article also highlights the threat that these signals pose to astronomy and the need for radio quiet zones to study deep space.
The article discusses the unique situation in the late 14th century when there were three popes. The origins of this predicament can be traced back to conflicts between the Church and the French monarchy. The schism lasted for 39 years until the Council of Constance in 1417, when a new Pope was elected and the schism was finally resolved.
The article explores the complex legacy of Thomas Jefferson, a founding father of the United States. While Jefferson is known for his contributions to equality and democracy, his participation in slavery and mistreatment of Indigenous communities raise questions about his legacy and whether historical figures should be judged by modern standards.
The article discusses wealth inequality in South Africa and explores the question of whether inequality is inevitable. It explains the use of the Gini index to measure inequality and highlights the limitations of this measure. The article also examines the role of government choices and economic systems in contributing to inequality, and discusses ways to reduce inequality, such as progressive taxes, transfers, and access to services. It concludes by emphasizing the global divide in wealth and power and the need to weaken the feedback loops that perpetuate inequality.
In this lesson, you embark on a thrilling adventure in Professor Ramsey's physics lab, where you must navigate the complexities of time travel after the professor accidentally steps through a time portal. To return to the present, you learn about Ramsey Theory and discover that a minimum of six chrono-nodules is necessary to guarantee the formation of a red or blue triangle, which will open a doorway back home, regardless of the random color connections. This exploration not only highlights the mathematical principles behind the challenge but also emphasizes the importance of systematic problem-solving in overcoming seemingly insurmountable obstacles.
The lesson discusses the innovative concept of space elevators as a potential alternative to traditional rocket launches for space travel. Space elevators could significantly reduce costs and improve safety and efficiency by using a fixed structure to transport payloads into orbit, with the possibility of lowering launch costs by up to 95%. While the idea has roots dating back to the 19th century, current advancements in materials and engineering, such as carbon nanotubes, are essential for overcoming the challenges of constructing such a massive structure, with several countries aiming to develop this technology by 2050.
The lesson explores the intricate world of atoms, highlighting their minuscule size and fundamental role as the building blocks of matter. It explains the composition of atoms, consisting of neutrons, protons, and electrons, and emphasizes the vast emptiness within them, filled with quantum fluctuations. Additionally, the lesson illustrates the simplicity and complexity of atomic structures, revealing how a few elementary particles can create a multitude of elements, while acknowledging the evolving nature of our understanding of atomic science.
This lesson explores the evolution and functioning of various types of light bulbs, highlighting their unique mechanisms for converting electrical energy into visible light. It covers incandescent and halogen bulbs, which use tungsten filaments; fluorescent bulbs, which utilize gas and a phosphorescent coating; vapor lamps for large area lighting; and LEDs, which operate on semiconductor technology. Understanding these differences enhances our appreciation for the science behind everyday lighting solutions.
The lesson explores the origins of the quirky "Ye Olde" signs, revealing that the "Y" actually represents the Old English letter "thorn," which was used to denote the "th" sound in words like "the." As printing technology evolved, the thorn letter fell out of use, leading printers to substitute "Y" for "th" due to its visual similarity, resulting in the playful yet historically inaccurate spelling we see today. Ultimately, these signs reflect a fascinating blend of linguistic history and printing practices.
In this lesson, we explore the intriguing question of what would happen if a giant ring were built around the Earth and its supporting poles were removed. The concept of symmetry breaking is introduced, explaining that if the ring is strong enough, it could potentially "hover" in place due to balanced forces, while a weaker ring might buckle and collapse. The lesson also touches on the idea of spinning, linking it to the Earth's rotation, and encourages further exploration of related topics.
The lesson explores the staggering size of the observable universe, which spans 93 billion light years and is approximately 100 quintillion times larger than Earth. To illustrate this vastness, a pixel comparison is used, where a single pixel represents Earth amidst an immense array of pixels symbolizing the universe, highlighting our planet's insignificance in the grand cosmic scale. Ultimately, it serves as a humbling reminder of our small place in the universe.
This lesson explores the intriguing mysteries of Earth's core, revealing that the inner core is a solid ball primarily composed of iron, with a temperature reaching around 9,800 degrees Fahrenheit. Scientists utilize seismology to study the core's structure, discovering a solid inner core and a molten outer core, while ongoing research aims to uncover the presence of other elements, such as sulfur, within this hidden realm. Overall, the lesson emphasizes the complexity and significance of Earth's core in understanding our planet's composition and history.
This lesson explains the significance of octane ratings in gasoline, which indicate how well fuel resists knocking during combustion. It emphasizes the importance of selecting the appropriate octane level for your vehicle to prevent engine damage, clarifies the reasons behind the higher cost of premium fuels, and discusses the role of ethanol in gasoline. Additionally, it highlights the differences between diesel and gasoline engines, underscoring the potential consequences of using the wrong fuel type.
This lesson explores the history, strategies, and advanced tactics of the classic game rock, paper, scissors, highlighting its origins from the Han Dynasty to its global popularity today. It provides practical tips for improving gameplay, such as understanding human psychology and employing counter tactics, while also introducing fun variations from different cultures. With these insights, players can enhance their skills and enjoy the game in new and exciting ways.
The Ryugyong Hotel in North Korea, an ambitious project intended to be the tallest hotel in the world, has stood unoccupied for over 33 years due to construction delays, financial issues, and engineering challenges. Initially envisioned to attract tourists and foreign investors, the hotel has become known as the "Hotel of Doom," symbolizing unfulfilled aspirations. Despite its troubled history, recent developments suggest a potential future opening, keeping hope alive for this iconic yet enigmatic structure.
The lesson on the eruption of Mount Vesuvius details the dramatic sequence of events leading up to and following the volcanic eruption that buried the towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring volcanic activity and the challenges of evacuating a densely populated area in the face of imminent danger. Ultimately, the tale serves as a reminder of nature's power and the resilience of communities in the aftermath of such disasters.
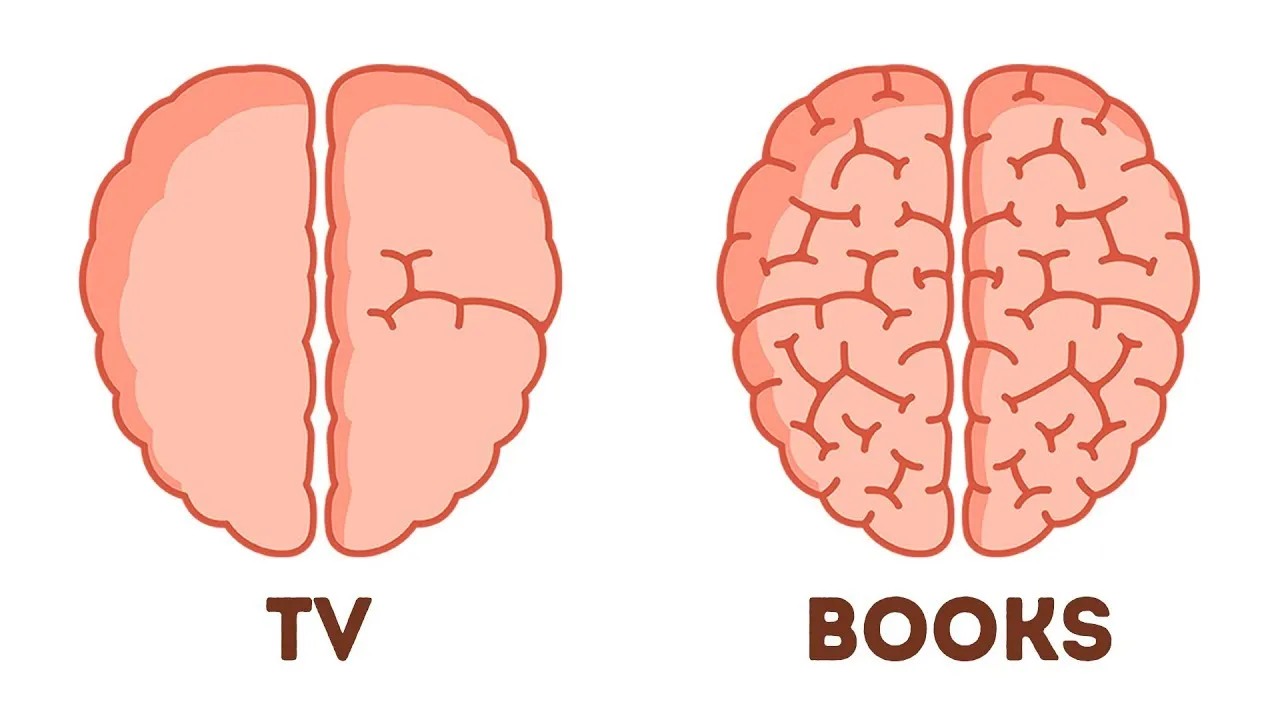
The lesson outlines several simple strategies to enhance brain power within a week, emphasizing the importance of sleep, stress management, hydration, and a balanced diet. It highlights the impact of love and maternal feelings on brain function, the benefits of engaging in creative activities like painting, and the cognitive advantages of reading. By incorporating these practices into daily life, individuals can significantly improve their mental sharpness and overall brain health.
This lesson explains the risks associated with cell phone batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries, which can explode due to overheating, overcharging, or physical damage. It outlines the causes of battery failures and provides practical tips for preventing explosions, such as using reliable chargers, avoiding extreme temperatures, and monitoring battery health. Additionally, it offers advice for extending battery life, emphasizing the importance of proper charging habits and regular maintenance.
This lesson focuses on a series of quick and easy one-minute stretching exercises designed to alleviate back pain, particularly for those who spend long hours sitting. It emphasizes the importance of stretching for overall health, flexibility, and muscle relaxation, and provides a variety of exercises, including knee twists, hip twists, and the cat-cow stretch, to strengthen and stretch the back and abdominal muscles. Participants are encouraged to incorporate these exercises into their daily routine to effectively manage and reduce back pain.
The lesson discusses the potential impact of living on Mars on human evolution, sparked by a question from Victor about how humans might adapt to life on another planet. It highlights the significant challenges of colonizing Mars, contrasting it with historical human settlements on Earth, and emphasizes that any evolutionary changes would occur slowly over time due to the harsh Martian environment. Ultimately, while the idea of a human colony on Mars is intriguing, it remains largely theoretical, with many obstacles to overcome before it could become a reality.
In "The Dishwashing Dilemma: Understanding Probability," the lesson explores how probability can help assess fairness in seemingly random selections, such as choosing which sibling does the dishes. Initially, the siblings agree on a random selection method, but as Bill is not chosen for multiple nights, they begin to question its fairness. Through calculations, the lesson illustrates that while a few nights without selection may seem normal, the probability of Bill not being picked for twelve nights in a row is low enough (about 3.2%) to warrant suspicion, highlighting the importance of understanding probability in evaluating random events.
In this lesson, we explored probability distributions using the example of flipping a fair coin three times, defining a random variable \(X\) that represents the number of heads obtained. We calculated the probabilities for each possible outcome (0 to 3 heads) and constructed a discrete probability distribution, illustrating how the probabilities are distributed across different outcomes. This exercise enhances our understanding of discrete probability distributions and the likelihood of specific results in random experiments.